There are affiliate links on this page.
Read our disclosure policy to learn more.
Ransomware Attack May 2017: Ooops, your files have been encrypted!
Ransomware is a growing threat in which malware is loaded on to your computer, tablet or phone and it locks access to your files unless you pay the
extortionist a ransom, by an untraceable and unrecoverable method, such as Bitcoin or other cryptocurrency or Western Union MoneyGram. Besides file
encryption, the malware can also steal files (Maze), force Windows machines to reboot into safe mode to bypass security software (Snatch), and halt other
computer processes (Zeppelin). May 12, 2017 saw a rapid spreading ransomware virus, spread by email.
If you received the email and clicked on the links, you saw a screen demanding payment of $300 worth of the online currency Bitcoin,
and a m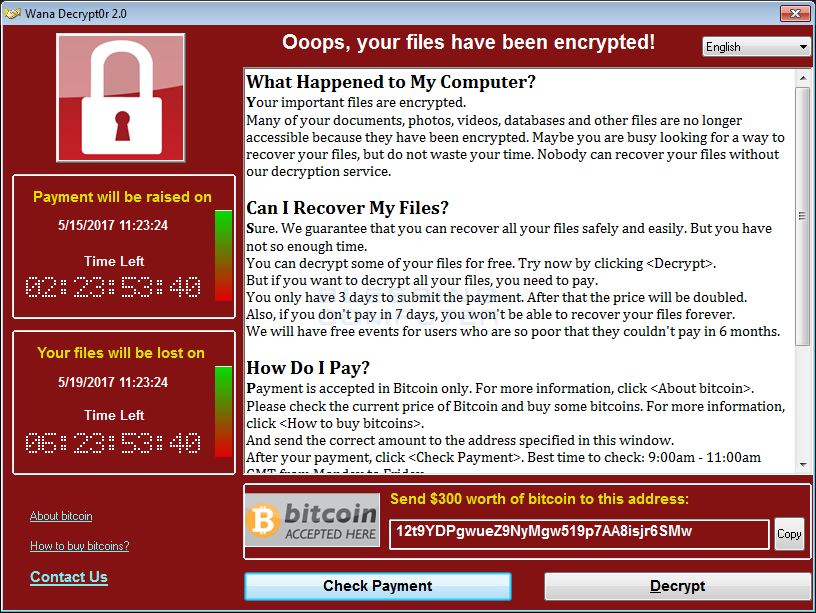 essage saying:
According to the Trend Micro Annual Security Roundup, ransomware-related threats exceeded 55 million in 2018 to over 61 million in 2019.
essage saying:
According to the Trend Micro Annual Security Roundup, ransomware-related threats exceeded 55 million in 2018 to over 61 million in 2019.
You can see examples and more information about specific types of ransomware here:
Key information if you click on a link
- The ransomware encrypts your computer's data (photos, files, etc.)
- You see a message similar to the one above, demanding a ransom to unlock it,
- The attacks use a malware similar to one called called Wanna Decryptor, also known as WannaCry. Wana Decrypt0r ransomware's name is WCry, but is also called WannaCry, WanaCrypt0r, WannaCrypt, or Wana Decrypt0r. WannaCry encrypts files with the following extensions, appending .WCRY to the end of the file name:
Who is at risk?
The ransomware seems to take advantage of a weakness in versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems which are not up to date on security patches. As of May 2017, there have been no reports ofd it affecting Apple computers, ipads or iphone nor Android cell phones.
How to prevent it
Make sure your computer's operating system has all current updates and security patches. In Windows,
- use the "Search Windows" in the bottom left corner to search for "check for updates" or
- go to Control Panel and navigate to Control Panel - All Control Panel Items - Security and Maintenance
- Make sure your security software is also updated We recommend Norton Security. See the boxes at right and see this page for all recommendations.
AND ABOVE ALL:
Make regular backups, of
- Important documents, files, photos, contact lists, etc. and
- System files.
By far the best way to do this is with a system image. A system image makes a complete backup of all files on a disk, including data, programs and system files. If something happens to your system, or even the C drive fails, you can reset the system and restore everything from the system image, which should be stored on a separate drive from the system drive.
You can make a system image from within Windows 10, in control panel. Search there for:
- Control Panel\System and Security\Backup and Restore (Windows 7)
System images are large files, so be sure to have a backup drive (either internal or attached externally) that has a lot of space on it (say at least 250 GB, of course, 500 GB or 1 TB would be better still)
You can find easy to follow, complete directions about making system image backups here on How to Geek how to Make System Images
Who has been affected?
- FedEx Corp.
- France's government cybersecurity agency warned French Internet users to take measures to protect themselves
- Russia's Interior Ministry says it has come under cyberattack.
- Hospitals in the U.K.
- Telecommunications companies in Spain
What to do if your computer has been ransomed
The best method is to use a professional service or professional software, like MalwareBytes or Symantec Norton Security.
It is critical that you install all available OS updates to prevent getting exploited by the MS17-010 vulnerability. Any systems running a Windows version that did not receive a patch for this vulnerability should be removed from all networks. If your systems have been affected, DOUBLEPULSAR will have also been installed, so this will need to also be removed.A script is available that can remotely detect and remove the DOUBLEPULSAR backdoor. Consumer and business customers of Malwarebytes are protected from this ransomware by the premium version of Malwarebytes and Malwarebytes Endpoint Security, respectively.
Symantec says (May 2017):
Decryption is not available at this time but Symantec is investigating. Symantec does not recommend paying the ransom. Encrypted files should be restored from back-ups where possible.
But Symantec also has a page providing their own detailed removal instructions here.
So, let's be clear; your encrypted files are gone, but you can remove the virus and make your computer safe for use again. Here is how:
For those who feel up to the challenge of going it alone, here are the general directions with links to more details. Encrypted files will have .WCRY appended to the end of the file names. The Trojan then deletes the shadow copies of the encrypted files. The Trojan drops the following files in every folder where files are encrypted: !WannaDecryptor!.exe.lnk and !Please Read Me!.txt.
- Turn off your pc.
- Restart your computer in Safe Mode.
Windows 10: Restart your PC. When you get to the sign-in screen, hold the Shift key down while you select Power Power icon > Restart.
After your PC restarts to the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
After your PC restarts, you'll see a list of options. Select 4 or F4 to start your PC in Safe Mode. Or if you'll need to use the Internet, select 5 or F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.
Windows 7: Turn on the computer and immediately begin pressing the F8 key repeatedly.
From the Windows Advanced Options Menu, use the arrow keys to select Safe Mode, and press ENTER. - On your desktop, delete all of the files labeled anything like WannaCry, WCry, WannaCry, WanaCrypt0r, WannaCrypt, or Wana Decrypt0r. See this YouTube video for more.
- Go to start and search for any other files with WannaCry in their names. Delete them. Some of them are in Users/AdminAppData/Local. Remove all the files other than the one you cannot that starts with FX in Users/AdminAppData/Local/Temp
- GZo to start, and open RegEdit. Editing this file is like performing brain surgery. See this YouTube for the changes to make.
- You should be able to restart your computer now in normal mode.
Who is behind the malware?
The Guardian, SlashDot, CNBC and NY Times are reporting that North Korea is behind the WannaCry ransomware. Kaspersky and Symantec both said on Monday that the North Korean cybergang known as Lazarus Group used very similar code. in 2015 and in the 2014 attack on Sony Pictures and an $81m heist on a Bangladeshi bank in 2016.